📂 Download MATLAB Code (Zip)
What Is Proper Orthogonal Decomposition (POD)❓
It is a mathematical method used to analyze and reduce the dimensionality of complex data sets. It is widely used in various fields, such as fluid dynamics, image processing, signal processing, and machine learning.
POD is a method of linear dimensionality reduction that aims to identify the most significant modes of variation in a data set. It does this by decomposing a given data set into a set of orthogonal basis functions, called the modes, which are ranked in order of their importance. The first mode captures the largest variation in the data, followed by the second mode, which captures the second-largest variation, and so on.
The POD algorithm involves performing a Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) on a data matrix to obtain the basis functions, or modes. These modes can then be used to reconstruct the original data with a reduced number of variables, while still retaining the essential features of the data. This dimensionality reduction can help simplify the analysis of complex data sets and make them more computationally efficient to work with.
POD has numerous applications, including image and signal compression, noise reduction, feature extraction, and data visualization. It is also used in fluid dynamics to analyze and predict the behavior of fluids, such as airflow over a wing or the flow of blood through the cardiovascular system.
POD is often used in model order reduction to extract the essential features or modes from high-dimensional data sets. These modes are then used to create a low-dimensional representation of the original system, resulting in reduced-order models that are computationally more efficient.
it is particularly useful in engineering applications, such as structural dynamics and fluid dynamics, where it can significantly speed up simulations and optimization studies while providing insights into the system’s underlying physics.
It is also used to perform simulations and optimization studies much faster than with the full-order model.
WHAT Is Radial Basis Function (RBF)❓
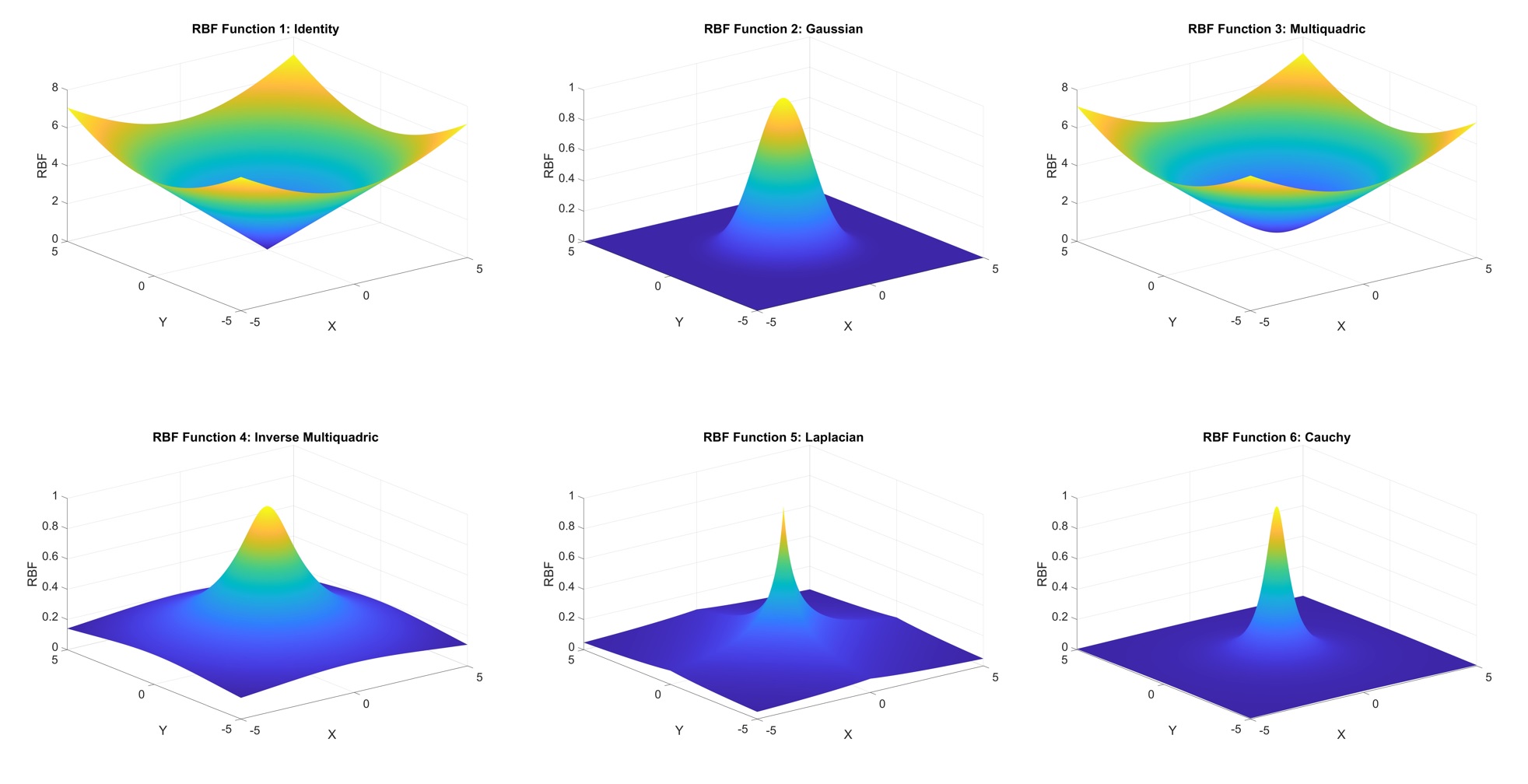
It is a method of constructing a function that fits a set of data points. It is a type of kernel-based interpolation that uses a set of basis functions centered on each data point to interpolate the function value at other points.
In RBF interpolation, the basis functions are typically chosen to be radial functions, such as Gaussian or inverse multiquadric functions. The parameters of these functions are determined by solving a linear system of equations that ensure that the interpolated function passes through each data point and has smoothness properties.
RBF interpolation has many applications, including function approximation, surface fitting, image processing, and computer graphics. One advantage of RBF interpolation is that it can be used with irregularly spaced data points, making it useful for problems where the data is not uniformly sampled. Additionally, RBF interpolation can handle data with noise or missing values by fitting a smooth function that passes through the available data points.
Radial Basis Function (RBF) interpolation has a wide range of applications in engineering problems, including design optimization, computational fluid dynamics, and structural analysis. Here are some ways that RBF is used for engineering problems:
Design optimization: RBF can be used to create surrogate models of complex simulations or experiments, which can then be optimized using gradient-based or evolutionary algorithms. This approach can reduce the computational cost of optimization problems that involve expensive simulations or experiments.
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD): RBF can be used to interpolate the flow field variables in CFD simulations, such as velocity and pressure, which can reduce the number of grid points required for accurate simulations. This approach is particularly useful for problems with complex geometries or time-varying flow fields.
Structural analysis: RBF can be used to interpolate the displacement field of structures, which can then be used to calculate stresses, strains, and other engineering quantities. This approach can reduce the computational cost of finite element analysis (FEA) simulations, particularly for problems with large deformation or contact.
Surrogate modeling: RBF can be used to create surrogate models of complex systems, such as electrical circuits or chemical reactors. These models can then be used to predict the behavior of the system under different operating conditions, without the need for expensive simulations or experiments.
What Is THE POD-RBF❓
The POD-RBF approach is a combination of Proper Orthogonal Decomposition (POD) and Radial Basis Function (RBF) interpolation, used for solving large-scale dynamical systems. It involves using POD to extract the most important features or modes from a high-dimensional data set, and RBF interpolation to reconstruct the dynamical system using these modes.
The first step of the POD-RBF approach is to perform a POD analysis on the data, which involves decomposing the data into a set of orthogonal modes that capture the dominant features of the system. The modes obtained from the POD analysis are then used to construct a low-dimensional representation of the original system.
The second step of the POD-RBF approach is to use RBF interpolation to reconstruct the dynamical system using the low-dimensional representation obtained from the POD analysis. This involves constructing a set of radial basis functions centered on the POD modes and solving a linear system of equations to determine the coefficients of these functions. The resulting RBF interpolation can then be used to predict the behavior of the system at any point in time.
The advantage of the POD-RBF approach is that it combines the accuracy of POD with the flexibility of RBF interpolation, resulting in a reduced-order model that is both accurate and computationally efficient. The approach is particularly useful for solving large-scale dynamical systems, such as those encountered in fluid dynamics and structural mechanics, where traditional simulation methods can be computationally expensive and time-consuming.
📓 Manuscript (Word.docx)
📑 Cite as
YUKI Algorithm and POD-RBF for Elastostatic and dynamic crack identification. Journal of Computational Science. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocs.2021.101451 .
BibTeX | EndNote | RefMan / Mendeley
Crack Identification Using Model Reduction based on Proper Orthogonal Decomposition coupled with Radial Basis Functions. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-016-1400-y
BibTeX | EndNote | RefMan / Mendeley
👁️🗨️ Read